Demonstration of multiple dissipative solitons with nickel-based metal organic framework saturable absorber
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53655/joe.g2252gKeywords:
Metal-organic framework, saturable absorber, dissipative soliton, pulse mode-locked laserAbstract
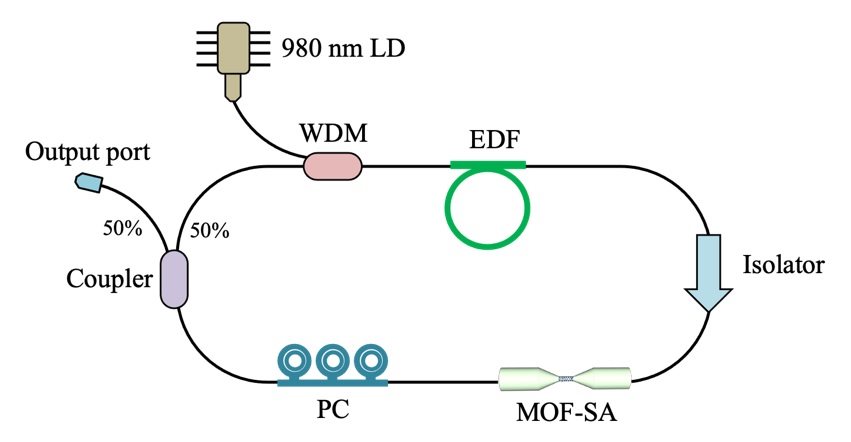
In this work, we have demonstrated the generation of dissipative soliton from single to multi-pulsing phenomenon. The generation of ultrashort pulses was achieved with nickel-based metal organic framework (Ni-MOF) as saturable absorber in a ring cavity erbium-doped fiber laser. The SA was fabricated by spin-coating Ni-MOF/polydimethylsiloxane composite on a tapered fiber substrate, which had an insertion loss of 2.82 dB, a modulation depth of 4.61 %, and saturation intensity of 30.12 MW/cm2. A self-started DS mode-locked pulse was observed at 1559.89 nm central wavelength with 3-dB bandwidth of 19.72 nm at threshold pump power of 33.5 mW. Its pulse width of 7.89 ps was recorded at 7.94 MHz repetition rate. The nature of pulse splitting was observed up to three pulses which were separated with 2.62 ns time spacing with the increment of pump power until 134.2 mW. The generated multiple dissipative soliton pulses realized in the laser cavity through Ni-MOF saturable absorber were stable and invariant for 1-hour stability measurement.
References
Y. Han, Y. Guo, B. Gao, C. Ma, R. Zhang, and H. Zhang, “Generation, optimization, and application of ultrashort femtosecond pulse in mode-locked fiber lasers,” Prog. Quantum Electron., vol. 71, p. 100264, May 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.pquantelec.2020.100264.
S. M. Kobtsev, “Artificial saturable absorbers for ultrafast fibre lasers,” Opt. Fiber Technol., vol. 68, p. 102764, Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2021.102764.
K. Y. Lau and D. Hou, “Recent research and advances of material-based saturable absorber in mode-locked fiber laser,” Opt. Laser Technol., vol. 137, p. 106826, May 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106826.
C. Lv et al., “Silver Nanowires with Ultrabroadband Plasmon Response for Ultrashort Pulse Fiber Lasers,” Adv. Photonics Res., vol. 3, no. 1, p. 2100184, Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1002/adpr.202100184.
B. Wang, H. Han, L. Yu, Y. Wang, and C. Dai, “Generation and dynamics of soliton and soliton molecules from a VSe2GO-based fiber laser,” Nanophotonics, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 129–137, Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1515/NANOPH-2021-0543/ASSET/GRAPHIC/J_NANOPH-2021-0543_FIG_009.JPG.
C. Huang, C. Wang, W. Shang, N. Yang, Y. Tang, and J. Xu, “Developing high energy dissipative soliton fiber lasers at 2 micron,” Sci. Rep., vol. 5, no. 1, p. 13680, Nov. 2015, doi: 10.1038/srep13680.
A.-P. Luo et al., “Buildup dynamics of dissipative soliton in an ultrafast fiber laser with net-normal dispersion,” Opt. Express, Vol. 26, Issue 3, pp. 2972-2982, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 2972–2982, Feb. 2018, doi: 10.1364/OE.26.002972.
L.-N. Duan, J. Wen, W. Fan, and W. Wang, “Generation of single and multiple dissipative soliton in an erbium-doped fiber laser,” Chinese Phys. B, vol. 26, no. 10, p. 104205, Sep. 2017, doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/26/10/104205.
N. Akhmediev, J. M. Soto-Crespo, P. Vouzas, N. Devine, and W. Chang, “Dissipative solitons with extreme spikes in the normal and anomalous dispersion regimes,” Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., vol. 376, no. 2124, p. 20180023, Jul. 2018, doi: 10.1098/rsta.2018.0023.
Y. Song, X. Shi, C. Wu, D. Tang, and H. Zhang, “Recent progress of study on optical solitons in fiber lasers,” Appl. Phys. Rev., vol. 6, no. 2, p. 021313, Jun. 2019, doi: 10.1063/1.5091811.
A. Murad et al., “Effect of nickel ion concentration on structural, optical and electrical properties towards Ni–H3BTC-MOF formation for nonlinear saturable absorption phenomenon,” J. Phys. Chem. Solids, vol. 167, p. 110743, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2022.110743.
M. A. W. Abdul Hadi et al., “Nano-tungsten trioxide saturable absorber for L-band noise-like pulse mode-locked fiber laser,” Opt. Fiber Technol., vol. 71, p. 102933, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2022.102933.
Q. Wang et al., “Wide spectral and wavelength-tunable dissipative soliton fiber laser with topological insulator nano-sheets self-assembly films sandwiched by PMMA polymer,” Opt. Express, vol. 23, no. 6, p. 7681, Mar. 2015, doi: 10.1364/OE.23.007681.
U. Brauch, C. Röcker, T. Graf, and M. Abdou Ahmed, “High-power, high-brightness solid-state laser architectures and their characteristics,” Appl. Phys. B, vol. 128, no. 3, p. 58, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.1007/s00340-021-07736-0.
M. A. Abdelalim, Y. Logvin, D. A. Khalil, and H. Anis, “Steady and oscillating multiple dissipative solitons in normal-dispersion mode-locked Yb-doped fiber laser,” Opt. Express, vol. 17, no. 15, p. 13128, Jul. 2009, doi: 10.1364/OE.17.013128.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Mohd Adzir Mahdi, AMIR MURAD, Norita Mohd Yusoff, Josephine Ying Chyi Liew, Mohd Hanif Yaacob

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.



